How to do an SEO Audit for a Website (Step-By-Step)-SEO

This search engine optimization (SEO) guide explains how to do an SEO audit for a website.
Below, you’ll learn how to perform an SEO audit that covers every detail of your site so you can identify errors that may be getting in the way of achieving your search engine optimization goals.
There’s also a section with additional resources that explain more about doing SEO auditing and the best tools for the job as well a link to a helpful checklist you can download and use during the process.
Please enable JavaScript
How to Do an SEO Audit
1. Run a Site Crawl
Your first task in learning how to do an SEO audit is to run a full site crawl to generate all the information you need on various aspects of your site, such as page titles, meta descriptions, header tags, image ALT text, broken links, and other on-page factors.
Tools such as Ahrefs Site Audit, Screaming Frog, and Semrush Site Audit are all excellent options for making this process as smooth as possible. Once you’ve run your site audit, you’ll have a wealth of data that will take the hard work out of completing most of the following steps in this guide.
2. Check for HTTPS Issues
HTTPS is a protocol to ensure data sent between websites and web browsers is securely encrypted. Google considers HTTPS a ranking signal, so you could be losing rankings without it.
As explained in our other guide with common technical SEO issues, you need to ensure HTTPS is enabled and the website is not encountering problems such as mixed content, which is when your site loads over an HTTPS connection but some resources (such as images and scripts) load over insecure HTTP.
3. Check for Indexing Issues
If a site is going to appear in the search results, it first has to be indexed by the search engines that provide those results.
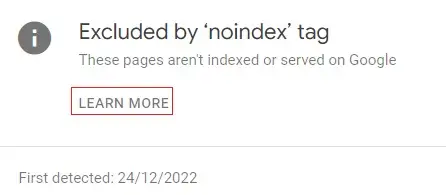
You can use Google Search Console to identify pages that haven’t been indexed and the reasons why by navigating to Indexing > Pages as you can see in the example image below.

Next, you want to click on each indexing issue listed, then click Learn More for Google’s instructions on how to fix them.
4. Check for Crawl Errors
Sticking with Google Search Console, your next task to perform an SEO audit for a website is to navigate to the Crawl Stats Reports.

If the website has any errors affecting Google’s ability to it, such as host server errors or broken links, they’ll be displayed here, and you click through to find out how to fix each one.
5. Check for Manual Actions
Manual actions are the official name Google gives to the penalties it doles out for violating its search engine guidelines. When doing an SEO audit, you need to look at that tab in Search Console to check whether or not a manual action has been applied to the site. If so, the necessary steps need to be taken to fix it.

6. Analyze Site Architecture and Navigation
Your site’s architectural structure and navigation have a direct impact on user experiences. Therefore, you need to ensure that your website’s architecture is easy to navigate and organized, as this helps search engines better understand your content and how to rank it.
Make sure each web page is at most a click depth of 3; meaning that it takes a user only 3 clicks to get to the page from the homepage. Also, ensure that all parent categories are listed in the main navigation menu and that child categories are assigned to the correct parent.
7. Analyze Speed and Performance
During your SEO audit, run the site through Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool to check the website’s speed and performance and receive recommendations on how to improve them.

8. Check for Mobile Responsiveness
Having a mobile-responsive website is crucial for providing a seamless user experience across different devices.
Along with physically testing your site on different devices, you can also run Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test or open up the developer tools in your search browser to check that your site is fully optimized for mobile.

Note: Google is retiring the Google Mobile-Friendly Testing tool on December 1, 2023, and encourages you to use Lighthouse in Chrome DevTools as a replacement, which is an open-source, automated tool for improving the quality of web pages. This tool offers audits for performance, accessibility, progressive web apps, SEO, and more.
9. Check and Fix Broken Links (404 Errors)
Broken links can lead to a poor user experience and lower search engine rankings. Google Search Console and the Ahrefs Broken Link Checker can help you identify broken links within your site. You can then check each one to find the root cause of the problem and fix it.

10. Check for Duplicate Content
The much-feared “duplicate content penalty” has long been debunked as a myth. However, the fact is that having the same content on multiple pages (or on multiple sites) can still cause problems as Google’s ranking algorithms have to decide which content to rank and, more often than not, will index the wrong content.
Siteliner from Copyscape is an excellent tool for identifying pages with duplicate content that you can then set about changing to ensure each page is unique.
11. Inspect the XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap is another invaluable tool for teaching search crawlers about your website and how the pages relate to each other.

First, open Search Console and go to Indexing > Sitemaps to ensure that you have an active sitemap in place. You can then locate it on your server and check that it’s properly configured for search engines to crawl and index your website’s most important pages.
12. Audit the Robots.txt File
A website’s robots.txt file tells search crawlers which sections of the site should be crawled and which ones should be ignored. A misconfigured robots.txt file is a common issue for on-site search engine optimization which is why it should be inspected during the SEO auditing process.
Make sure important directories, files, and web pages are not being blocked with the Disallow directive and that the sitemap location is listed in the robots.txt file using the correct rule: Sitemap: https://domain.com/sitemap.xml
13. Analyze Schema Markup
Schema Markup is a type of structured data that gives search engines valuable information about the type and topic of your content.
Use Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to assess whether your pages have Schema Markup that is accurate, relevant, and optimized to help you appear in rich results like Featured Snippets.

14. Check the Title Tags
A well-optimized title tag can make all the difference to your SEO success, ensuring that both search engines and their users understand the subject of your content and its relevance to search queries.
Any site auditing tool you decide to use will identify issues of missing or duplicate title tags that must be attended to. As part of the auditing process, you’ll also need to check that each title tag uses your primary keyword and accurately describes the content of the page.
See our free on-page SEO checklist and template page for more details on this step and the other items below that reference on-site optimization.
15. Analyze the Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions provide a brief summary of a page’s content and can influence a user’s decision to click through to the page from the search results.
As part of your SEO audit, you should be checking that each page has a meta description of around 150-160 characters that includes your primary keyword and a compelling call-to-action (CTA) convincing visitors to click through to the page.
16. Check the URL Structures
Another essential part of learning how to do an SEO audit for a website properly is to check that the URLs are SEO-friendly; meaning they’re short, concise, and match the primary target keyword for the page.
Start by reviewing the URLs of the top-ranking pages. Look for URLs that are too long, contain irrelevant numbers, words, and characters, or don’t accurately describe the content of the page. These are signs that the URL structure may need to be optimized.
Next, check for consistency in your URL structure. All of your pages should follow a similar URL format with hyphens separating words.
17. Audit the Header Tags (H1)
H1 header tags are essential for helping users and search engine crawlers alike understand what your content is about.

Tools like Semrush and the Ahrefs Site Audit can be used to identify any pages that are missing H1 tags so that you can quickly add them.
You should also be on the lookout for duplicate header tags, as these will do almost as much damage as having no title tags. For best results, optimize your H1 tags by ensuring they’re an exact match of your title tag.
18. Audit the Subheader Tags (H2-H6)
Subheadings give your content structure, making it easier for users to read and search engine crawlers to understand the key information on the page.
Therefore, when you’re performing an SEO audit, you should ensure that every page follows an appropriate subheading structure, with main points divided into sections by H2 tags, and those sections divided further with H3 tags. H4 tags should go under the H3 tags, and so on down the levels.
Header tags can also help you improve your rankings for relevant search terms, so you’ll benefit from optimizing the H2 tags for the target SEO keywords and the H3 tags with keyword variations and synonyms to improve topical relevance.
19. Analyze Keyword Usage and Density
Keywords may be the foundation of your SEO, but they’ll only benefit your site if they’re used appropriately.
Ensure that the primary target keyword is used in the page title, meta description, H1 tag, a single H2 subheading, and a few times throughout the main body content, aiming for a keyword density of 1-2%.
Again, Semrush and Ahrefs can help with this SEO auditing process for keyword usage and density as well as WordPress plugins like Yoast SEO and Rank Math.
20. Check Image Optimization
When it comes to image optimization during an SEO audit, check the following items:
- Image file sizes are as small as possible to improve page speed.
- Each image has a descriptive, keyword-optimized ALT text to improve usability and SEO signals.
- Image filenames match the target keyword for SEO.
- Optimal file formats and dimensions for each type of visual content. For example, pictures should be saved as JPEGs while infographics should be PNGs.
21. Check Content Quality and Relevance
“Content is King” may be a cliche these days but, like all cliches, it’s one that’s grounded in truth when it comes to search engine optimization and keyword rankings.

As you conduct your SEO content audit, check that each article:
- Is relevant to the focus keyword.
- Aligns with search intent.
- Is valuable and informative.
- Is accurate and up-to-date.
- Uses relevant internal links.
- Is optimized for readability.
22. Analyze Internal Links and Anchor Text
Running a site crawl will identify any broken internal links in your site, but that’s not all you want to be looking out for.
Your SEO audit should also include:
- Checking for orphan pages that have no internal links to them and adding new links to those pages.
- Ensuring anchor text is keyword-rich, relevant, and descriptive.
- Making sure that your website has a clear and logical internal linking structure, with your most important pages easily accessible from your website’s navigation menu.
23. Audit the User Experience
Along with mobile-friendliness, site speed, and navigation (all of which are covered separately in this SEO audit instruction guide), you’ll also want to consider the following to ensure you’re providing users with the best possible on-site experience:
- Is the content well structured with headings and bullet points?
- Is it easy to read with good font size and color choices?
- Would a general user feel satisfied if they landed the page? Or would they need to visit other web pages to fully satisfy their search intent?
- Is there an opportunity to conduct user testing, asking people to perform certain tasks on the website and observe how they interact with it?
24. Audit the Backlink Profile
Backlinks (literally links back to your website from third-party sources) provide signals to search engines about the quality, relevance, and authoritativeness of your content, which are major ranking factors for Google.
Tools like Semrush and Ahrefs can be used to generate a comprehensive backlink profile that provides valuable data about your referring domains, their Domain Authority and Page Authority scores, and whether the incoming links are dofollow or nofollow.
These SEO auditing tools can help you make informed decisions when it comes to purging your website’s backlink profile of toxic or harmful links and identifying new opportunities to generate more high-quality inbound links to improve SEO ranking performance.
Also, see our free off-page SEO checklist and template page for more details on this step and the other items below that reference off-site optimization.
25. Analyze the Backlink Anchor Text Distribution
While focusing on backlinks, an anchor text distribution checker is a good tool to use to analyze the anchor text ratio for incoming links. You can then make sure each page is following a good anchor text ratio that looks natural to search engine algorithms or take the necessary steps to fix it.
Here’s a good strategy to follow for this part of the SEO audit process as explained in our other guide anchor text optimization best practices:
Homepage Backlinks Anchor Text Ratio
- 80-95% mix of branded, natural, and URL anchor text.
- Up to 10% with partial and phrase match keywords included in anchor text.
- Up to 5% with exact match keyword anchor text.
Inner Page Backlinks Anchor Text Ratio
- 35-45% mix of branded, natural, and URL anchor text.
- 50-60% with partial and phrase match keywords included in anchor text.
- Up to 10% with exact match keyword anchor text.
26. Audit Online Reputation and Reviews
Are customers heading online to review their experience with your business? If so, where are they leaving these reviews, and what are they saying?
More importantly, your SEO audit should clarify that someone in your business is taking responsibility for replying to those reviews in a timely, friendly, and professional manner.
27. Audit Local Business Listings
Business listings are essential to local SEO efforts, helping the organization get noticed whenever someone searches for similar businesses in a specific geographical location.
At this stage of the audit, you should be checking that the business has a fully-optimized presence on all major business listing platforms like Google Business, Bing Places, and Apple Business Connect.
28. Check for NAP Consistency (Name, Address, Phone Number)
While reviewing local SEO profiles, double-check that the NAP information is present, accurate, and consistent across all platforms. Every element should be the same across third-party business listing sites, including abbreviations and suite numbers used in the address.
This also goes for the website URL, email address, and social links. If your site, for example, resolves to the HTTPS versions without the www (e.g., https://domain.com), then make sure that is how it is listed on the third-party sites.
29. Check for Localized Content
Businesses targeting customers in specific locations, should have localized content on the website tailored to significantly improve organic visibility in local search results.
The site crawl you ran at the very start of this process will give you a comprehensive overview of all the content on the site. You can use this data to identify if enough localized content has been created, then run on-page optimization tools to ensure that content is well-optimized for its target search terms.
If not, updates need to be made to the on-page SEO signals and/or more content should be published to rank for local SEO keywords that attract the right target audience for the business.
30. Find New Keyword Opportunities
The final step of the SEO audit process is to utilize keyword research best practices, looking for new opportunities to increase the search visibility of your fully audited and optimized website.
You can use a multitude of paid and free tools for this process like Google’s Autocomplete featrue, Ahrefs free keyword generator (seen below), social media monitoring tools, Google Trends, etc. (See this related guide with a complete list of strategies to find good keyword opportunities for your website.)

During this final stage of the SEO audit, you want to focus on finding long-tail keywords for more qualified traffic, and pay close to the search volume and ranking difficulty of each new opportunity to determine its value to your SEO campaigns.
Learn More About SEO Audits
The links below explain more about SEO auditing. Use these resources to expand your knowledge on the subject.
Do an SEO Audit Summary
We hope you enjoyed this guide explaining how to do an SEO audit for a website.
As you discovered, the process for how to perform an SEO audit consists of multiple steps to properly analyze and check all of the factors that can impact the search engine rankings and organic visibility of a website. By following the tasks outlined in this guide, you’ll ensure that the SEO audits you do cover the essential elements for on-site and off-site SEO.

The Editorial Staff at SEO Chatter is a team of search engine optimization and digital marketing experts led by Stephen Hockman with more than 15 years of experience in search engine marketing. We publish guides on the fundamentals of SEO for beginner marketers.
#SEO #Audit #Website #StepByStep





