Large cracks push imperilled Antarctic glacier nearer to cave in

Large fractures within the floating ice of Antarctica’s large Thwaites Glacier — a fast-melting formation that has grow to be an icon of local weather alternate — may shatter a part of the shelf inside of 5 years, analysis suggests. If that occurs, in what have been regarded as a slightly solid a part of Thwaites, the glacier may free up an armada of icebergs and start flowing a lot quicker into the sea, funnelling ice that have been resting on land into the ocean, the place it might give a contribution to sea-level upward thrust.
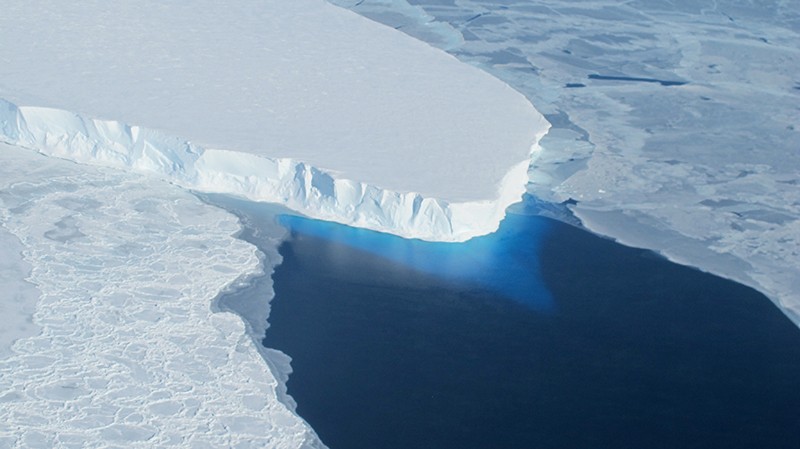
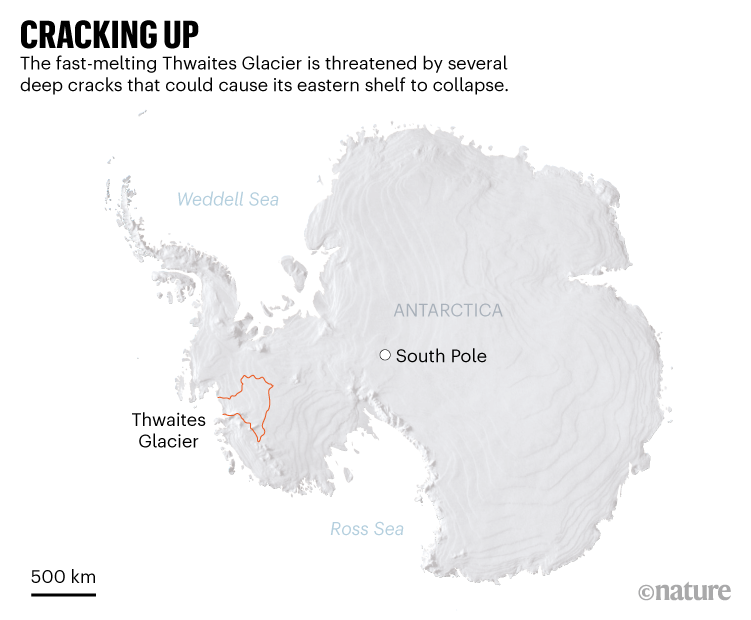
For many years, scientists have in moderation tracked adjustments within the Thwaites Glacier, which already loses round 50 billion tonnes of ice each and every 12 months and reasons 4% of world sea point upward thrust. The not too long ago known fractures are deep, fast-moving cracks in Thwaites’ japanese ice shelf (see ‘Cracking up’). They gave the impression in satellite tv for pc pictures during the last few years and their expansion appears to be accelerating.
“I visualize it reasonably very similar to that automobile window the place you may have a couple of cracks which can be slowly propagating, after which you pass over a bump on your automobile and the entire thing simply begins to shatter in each and every route,” mentioned Erin Pettit, a glaciologist at Oregon State College in Corvallis, on the American Geophysical Union (AGU) assembly on 13 December. If Thwaites’ japanese ice shelf collapses, ice on this area may drift as much as thrice quicker into the ocean, Pettit says. And if Thwaites have been to cave in totally, it might elevate sea ranges through 65 centimeters.
Breaking point of alternate
Pettit will describe the paintings on 15 December on the AGU assembly in New Orleans, Louisiana. It’s the newest discovering from the five-year, US$50-million Global Thwaites Glacier Collaboration, an initiative funded through the USA and UK governments to check and perceive the specter of how Thwaites might contribute to rising sea levels in a warming global.
“We’ve got been anticipating that ice shelf to fail, and that’s one of the crucial causes that there was any such coordinated world effort to check Thwaites — it’s large and vital, however it’s additionally been obviously poised getting ready to alternate,” says Kirsty Tinto, a geophysicist on the Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory in Palisades, New York, who has studied Thwaites. The newest paintings, she says, finds extra about how ice cabinets fail. “Figuring out the ones processes is helping us to grasp now not simply Thwaites, but in addition the entire remainder of Antarctica, previous, provide, and long run,” she says.
Mountain brace
Thwaites flows off the Antarctic continent into the Southern Ocean. At 120 kilometres throughout, it’s the global’s widest glacier. Throughout about two-thirds of that expanse, ice flows slightly temporarily into the sea. The remainder one-third is the japanese ice shelf, the place ice have been flowing slightly slowly1. Partially, that’s since the ice grinds to a halt when it reaches an underwater mountain about 40 kilometers offshore. The submerged mountain holds again the ice drift like a cork in a bottle.
Previous this 12 months, contributors of the Thwaites collaboration reported that the glacier is turning into unstuck from that mountain, inflicting cracking and fracturing throughout different portions of the ice shelf23. Earlier research4,5 have additionally proven hints of instability throughout Thwaites’ japanese ice shelf. “It’s been one thing to control for a very long time,” says Matthew Siegfried, a glaciologist on the Colorado College of Mines in Golden, Colorado.
The fractures stuck the eye of Pettit and her colleagues two years in the past, as they have been taking a look thru satellite tv for pc pictures to determine the place to arrange camp for the season. One crack, nicknamed ‘the dagger’, was once even headed instantly in opposition to the proposed camp website. It wasn’t shifting speedy sufficient for the scientists to relocate their paintings, however “we in fact all simply needed to take a pause”, mentioned Pettit. “It nonetheless was once vastly sudden to me that this was once hastily converting that speedy.”
The fractures are propagating in the course of the ice at speeds of a number of kilometres in step with 12 months. They’re heading into weaker and thinner ice, the place they are going to boost up and result in the loss of life of this a part of the Thwaites ice shelf inside of 5 years, Pettit estimates.
“There’s going to be a dramatic alternate within the entrance of the glacier,” mentioned Ted Scambos, a glaciologist on the Cooperative Institute for Analysis in Environmental Sciences in Boulder, Colorado. “It’ll boost up the tempo and successfully widen the harmful a part of the glacier.”
Heat water flows
How precisely the adjustments may occur isn’t transparent, says Siegfried, as a result of many components affect how ice cabinets fall aside. The ones come with how hastily heat water melts the ground of the floating a part of the glacier, and the geometry of ways ice, land and water engage.
Probably the most collaboration’s contemporary discoveries at Thwaites is that ocean tides motive the floating a part of the glacier to stand up at prime tide and drop down at low tide. That up-and-down ‘tidal pumping’ — lengthy suspected however infrequently noticed intimately — reasons the glacier to flex additional upstream, together with within the area the place it flows off land and into the water. Seismic and radar knowledge from the Thwaites paintings have proven that as a result of this flexing, heat water could possibly interfere underneath the glacier extra simply, mentioned Lizzy Clyne, a glaciologist at Lewis & Clark School in Portland, Oregon. “The lifestyles and conceivable speedy formation of those options will have implications for the long-term balance of the ice shelf,” they mentioned.
The Thwaites collaboration finished its maximum intensive box analysis season in 2019–20, prior to the COVID-19 pandemic interrupted the venture ultimate 12 months. This Antarctic wintry weather, which is below means, a number of analysis groups are once more descending onto the ice to take measurements at other places around the glacier.A big analysis cruise in February aboard the USA icebreaker Nathaniel B. Palmer will even find out about the sea at once in entrance of the glacier’s floating edge.
Every talk over with underscores how briskly Thwaites is converting. Seeing this large ice shelf shifting at you at a couple of mile once a year is unsettling, mentioned Scambos. “And all on its own, this one glacier is huge sufficient to have an effect on sea point considerably.”
#Large #cracks #push #imperilled #Antarctic #glacier #nearer #cave in