Document-breaking simulation hints at how local weather formed human migration

A colossal simulation of the previous two million years of Earth’s local weather supplies proof that temperature and different planetary prerequisites influenced early human migration — and perhaps contributed to the emergence of the modern day human species round 300,000 years in the past.
The discovering is one of the to return out of the most important fashion to this point to research how adjustments in Earth’s motion have influenced local weather and human evolution, revealed in Nature1 lately. “That is any other brick within the wall to reinforce the function of local weather in shaping human ancestry,” says Peter de Menocal, director of the Woods Hollow Oceanographic Establishment in Falmouth, Massachusetts.
The concept local weather may have an important function in human evolution has been round since no less than the Nineteen Twenties2, when scientists began debating whether or not drier prerequisites had led early human ancestors to start strolling on two toes, to evolve to existence at the savannah. However to this point, researchers have struggled to supply robust proof that local weather performed an element in shaping humanity.
Orbital affect
In the newest learn about, Axel Timmermann, a local weather physicist at Pusan Nationwide College in South Korea, and his colleagues ran a local weather fashion on a supercomputer for 6 months to reconstruct how temperature and rainfall may have formed what sources have been to be had to people during the last few million years. Particularly, the researchers tested how long-term fluctuations in local weather led to via Earth’s astronomical motion may have created the prerequisites to spur human evolution.
The rush and pull of alternative planets alters Earth’s local weather via converting each the planet’s tilt, and the form of its orbit. Over 41,000-year cycles, Earth’s tilt oscillates, affecting the depth of seasons and converting how a lot rain falls over the tropics. And over 100,000-year cycles, Earth is going from having a extra round orbit — which brings extra daylight and longer summers — to having a extra elliptical orbit, which reduces daylight and may end up in sessions of glacial formation.
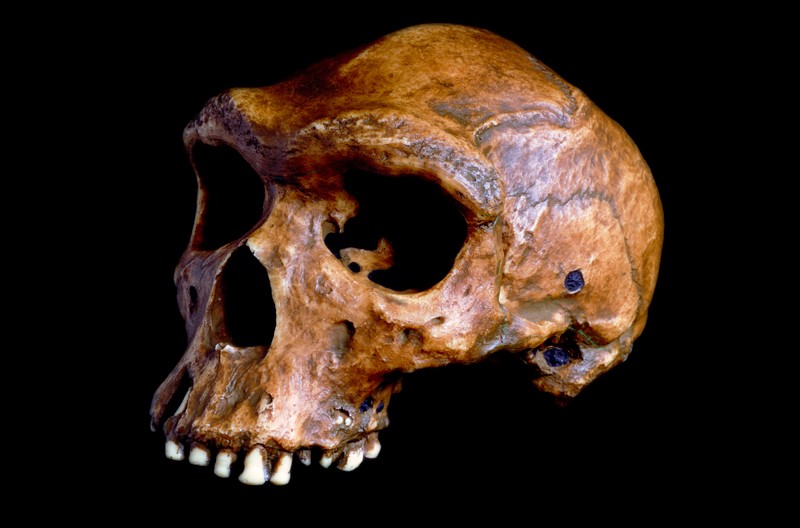
Timmermann and his colleagues used a simulation that included those astonomical adjustments, after which blended their effects with 1000’s of fossils and different archaeological proof to determine the place and when six species of people — together with the early Homo erectus and the trendy Homo sapiens — can have lived.
Actions and combining
The learn about pumped out a dizzying quantity of knowledge, and Timmermann says that a number of fascinating patterns emerged. As an example, the researchers’ research confirmed that an early human species, Homo heidelbergensis, began increasing its habitat round 700,000 years in the past. Some scientists have idea that this species may have given upward push to a slew of others around the globe, together with Neanderthals (Homo neanderthalensis) in Eurasia and H. sapiens someplace in Africa.
The fashion means that the distribution of H. heidelbergensis around the globe used to be conceivable as a result of a extra elliptical orbit created wetter local weather prerequisites that allowed the species emigrate extra broadly. The simulation additionally confirmed that essentially the most liveable areas, when it comes to local weather, shifted through the years, and the fossil report tracked in conjunction with them.
“The worldwide number of skulls and gear isn’t randomly allotted in time,” Timmermann says. “It follows a trend” that overlaps with local weather alternate pushed via Earth’s motion. “That is superb to me — here’s a trend that no person to this point used to be ready to peer.”
One a part of this trend may supply recent perception into the place and the way our personal species emerged. Some genetic research of modern day hunter-gather teams in sub-Saharan Africa — who have a tendency to be genetically remoted — counsel that H. sapiens is the end result of a unmarried evolutionary match in southern Africa. However different research level to a extra advanced tale, by which humanity started as a hotchpotch of many alternative teams of historic Africans that, in combination, developed into modern day people.
Timmermann and his colleagues say that their local weather reconstruction favours the single-evolutionary-path speculation. The fashion means that our species developed when H. heidelbergensis in southern Africa began dropping habitable habitat right through an strangely heat duration. This inhabitants can have developed into H. sapiens via adapting to the warmer, drier prerequisites.
However this discovering is not going to finish debate. “To make the case {that a} explicit local weather match resulted in a speciation match is in reality exhausting”, partially on account of gaps within the fossil and genetic report, says Tyler Religion, a palaeobiologist on the College of Utah in Salt Lake Town.
The similar is going for most of the different patterns reported within the paper. “The individuals who’ve spent a profession learning this may increasingly both be in violent settlement or war of words with the propositions right here,” de Menocal says. The fashion, then again, is a “out of the ordinary accomplishment in and of itself” and “offers you a template to invite those questions”.
Maximum researchers that spoke to Nature say that extra proof shall be had to turn out that astronomical cycles influenced the trajectory of human ancestry. “If fixing the thriller of local weather alternate and human evolution might be handled in a single paper, it might had been executed 40 years in the past,” Religion says.
Which is why Timmermann and his colleagues are making plans to run even greater fashions, together with ones that combine genetic information.
#Recordbreaking #simulation #hints #local weather #formed #human #migration